Contract Definition
Contract
Base Contract
The contract from which other contracts inherit features
Sub Node
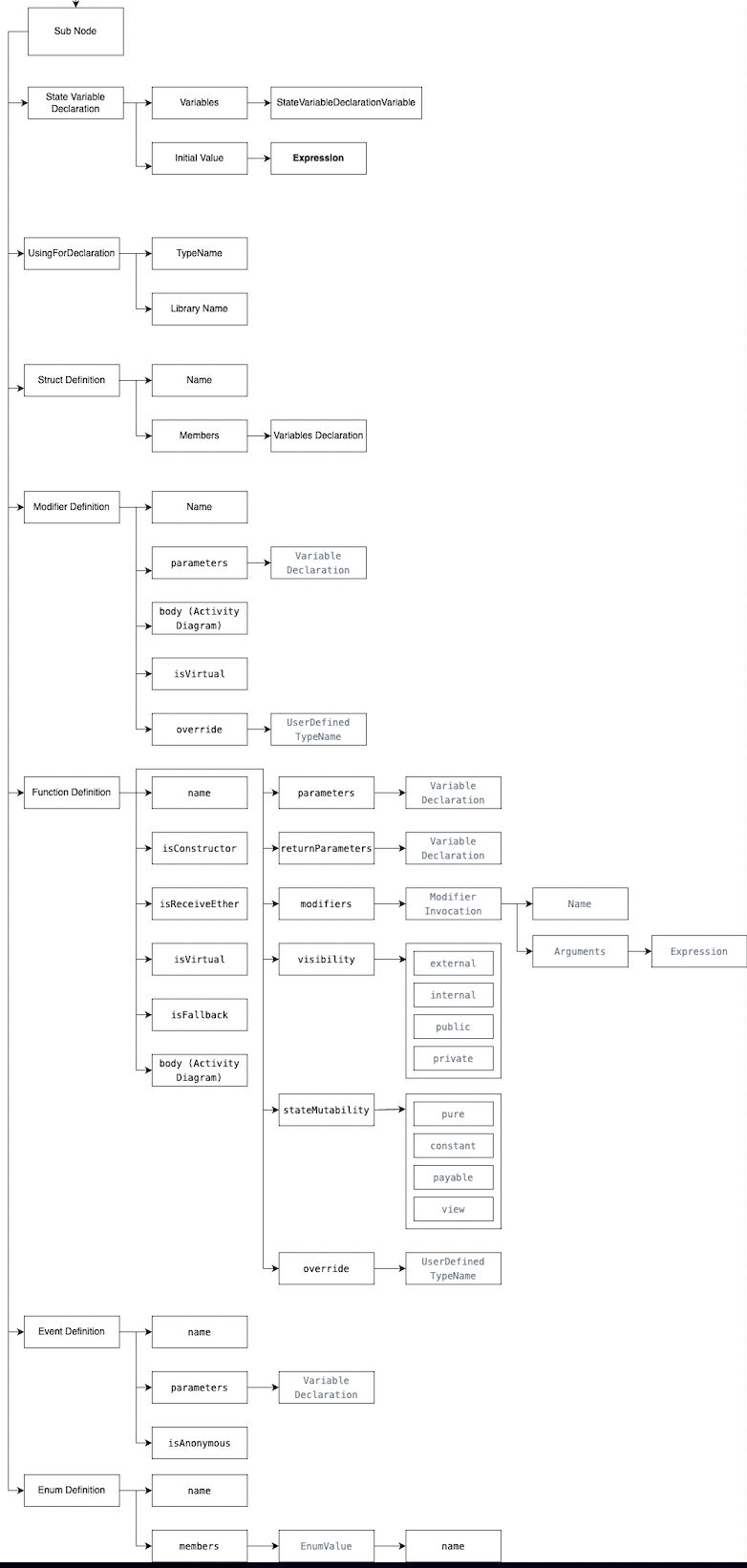
State Variable Declaration
State variables of contracts are stored in storage in a compact way such that multiple values sometimes use the same storage slot
Variables:
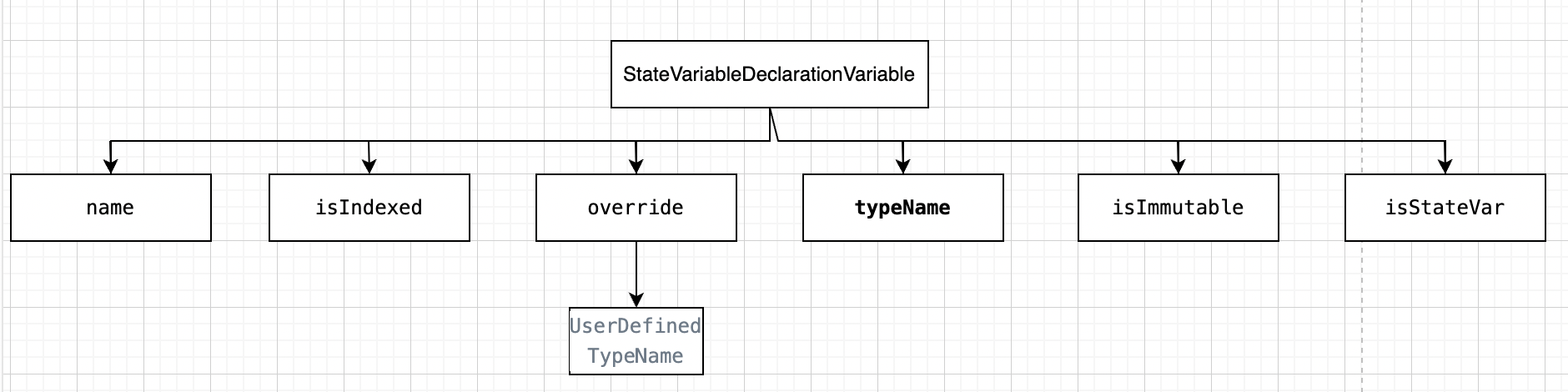
StateVariableDeclarationVariable:
state or local variable type needs to be specified during declaration. Each declared variable always have a default value based on its type.
Initial Values:
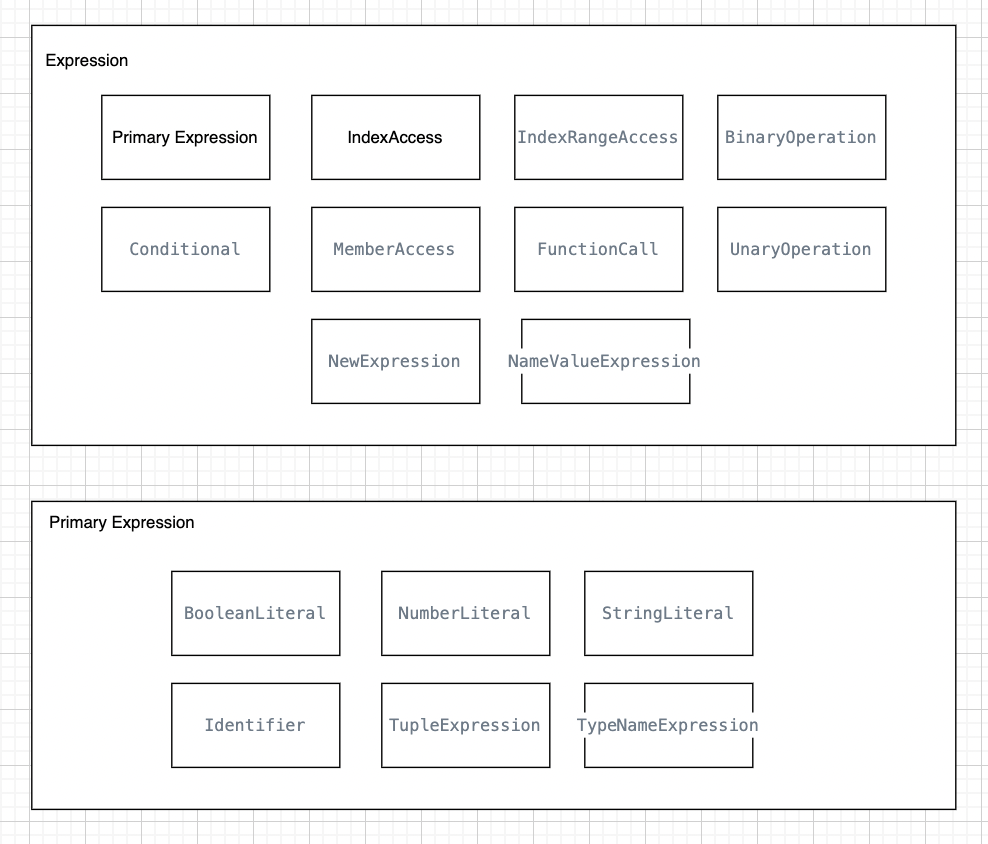
Expression:
A statement (comprising multiple operands and optionally zero or more operators) that results in a single value, object, or function. The operand can be a literal, variable, function invocation, or another expression itself.
Using for Declaration
Declaration to inherit any existing
- TypeName: inherited type name of a contract
- Library Name: inherited library name of a contract
Struct Definition
Allows you to create more complicated data types that have multiple properties
- Name: name of the properties
- Members: members of related properties
Modifier Definition
A function modifier is a compile-time source code roll-up. It can be used to amend the semantics of functions in a declarative way. From this definition, we can understand that a modifier aims to change the behaviour of the function to which it is attached, including:
Name: Name of the modifier
Parameters: Parameters of the modifier:
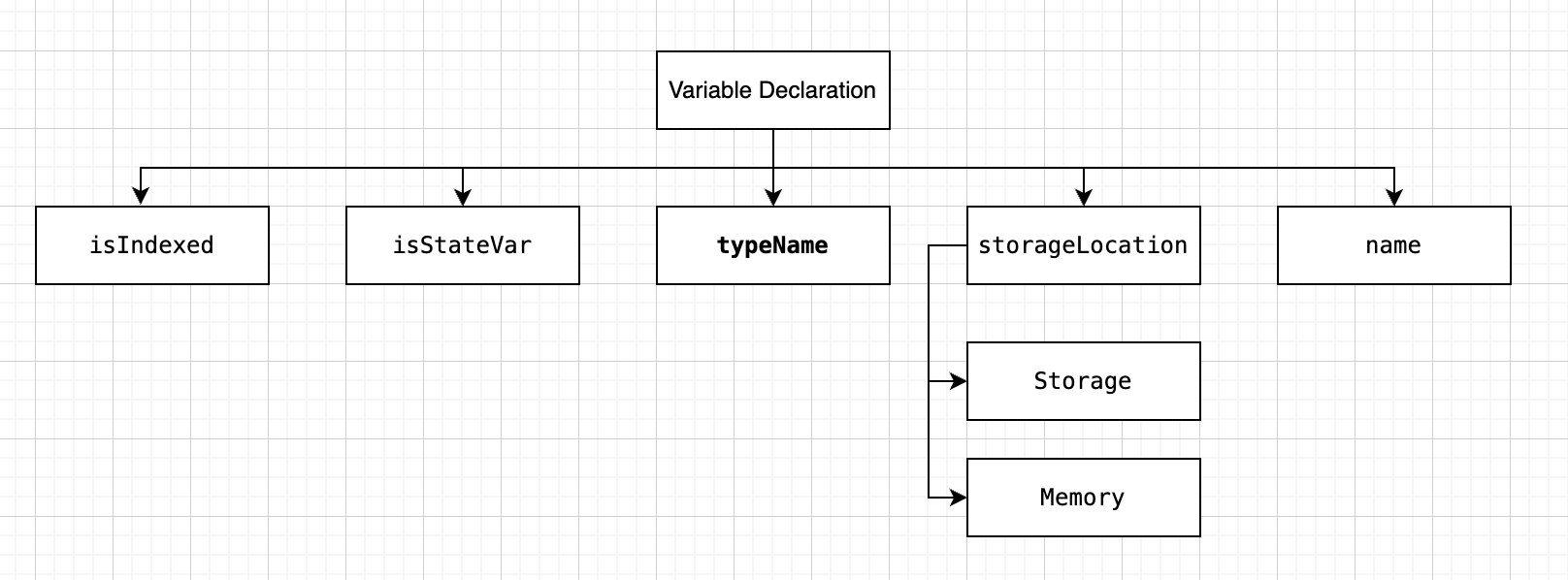
Variable Declaration:
parameters variable declared as a default vale
Body (Activity Diagram):
Block:
Block of code and related with the activity diagram
Statements:
multiple lines of instructions inside activity diagram
Statement:
Single instruction inside activity diagram, it might have the form of
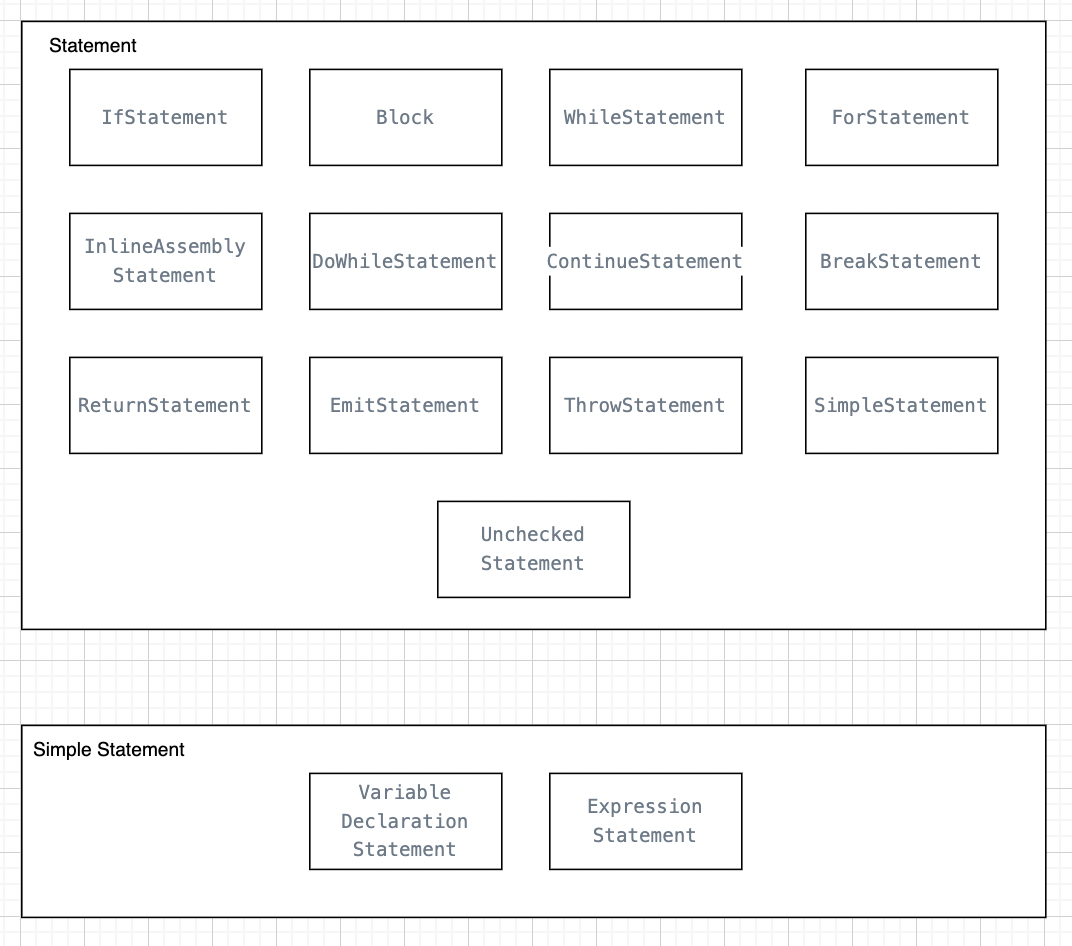
IfStatement:
The schema described within the If clause is evaluated against the logic inside activity diagram
Block:
Block inside schema described and evaluated inside activity diagram
WhileStatement:
While block inside schema described and evaluated inside activity diagram
ForStatement:
For block inside schema described and evaluated inside activity diagram.
InlineAssemblyStatement:
Inline assembly block inside schema described and evaluated inside activity diagram
DoWhileStatement:
Do-While block inside schema described and evaluated inside activity diagram
ContinueStatement:
Continue block inside schema described and evaluated inside activity diagram
BreakStatement:
Break block inside schema described and evaluated inside activity diagram
ReturnStatement:
Return value block inside schema described and evaluated inside activity diagram
EmitStatement:
Emit block inside schema described and evaluated inside activity diagram
ThrowStatement:
Throw block inside schema described and evaluated inside activity diagram
SimpleStatement:
VariableDeclarationStateme:
Variable declaration block inside schema described and evaluated inside activity diagram
ExpressionStatement:
Expression block inside schema described and evaluated inside activity diagram
UncheckedStatement:
Unchecked block inside schema described and evaluated inside activity diagram
isVirtual:
The function in the parent contract needs to be declared with the keyword virtual to indicate that it can be overridden in the deriving contract.
Override:
Change how a function in the parent contract is implemented in the derived class
UserDefinedTypeName:
Custom defined type name for the override function
Function Definition:
Name:
Name of a given function
isConstructor:
A special function declared using constructor keyword. It is an optional funtion and is used to initialize state variables of a contract
isReceiveEther:
In order to receive ethers in Solidity (or any other native coin in any EVM blockchain), we need to create a receive() function with the payable modifier
isVirtual:
The function in the parent contract needs to be declared with the keyword virtual to indicate that it can be overridden in the deriving contract
isFallBack:
An external function with neither a name, parameters, or return values. It is executed in one of the following cases: If a function identifier doesn't match any of the available functions in a smart contract. If there was no data supplied along with the function call.
Body (Activity Diagram):
Block of code and related with the activity diagram
Parameters:
Variable Declaration:
isIndexed:only relevant to logged events. From Contracts - Events: Up to three parameters can receive the attribute indexed which will cause the respective arguments to be searched for: It is possible to filter for specific values of indexed arguments in the user interface
isStateVar:Values of these variables are permanently stored in the contract storage.
TypeName:Type of declared variable
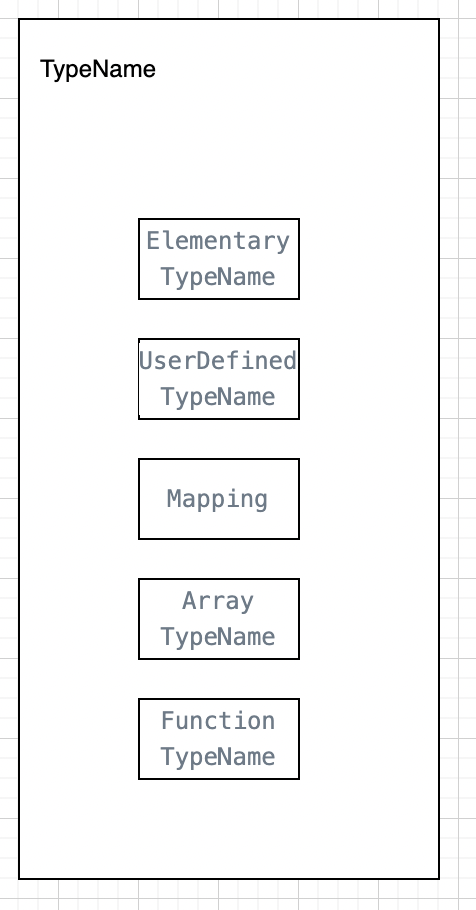
Elementary TypeName:
Basic type for solidity
UserDefinedTypeName:
Custom type for solidity
Mapping:
Reference (in a way where it works as a hash table) type as arrays and structs.
ArrayTypeName:
data structure, which stores a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type
FunctionTypeName:
the types of functions. Variables of function type can be assigned from functions and function parameters of function type can be used to pass functions to and return functions from function calls
StorageLocation:Storage:
database data stored in a blockchain node file system. It is persistent and has access to multiple executions of the same contract
Memory:
to store data for the execution of a contract. It holds functions argument data and is wiped after execution
Name:Name of the variable
returnParameters:
functions that return parameter list and are not taken for overlad resolution.
Modifiers:
modify the behaviour of a function
Modifier Invocation:
Name:
name of the invoked modifier
Arguments:
arguments of the modifier
Visibility:
Control who has access to the functions and state variables in your contract and how they interact with them
External:
can only be called from a third party. It cannot be called from the main contract itself or any contracts derived from it
Internal:
can be called by the main contract itself, plus any derived contracts
Public:
can be called from all potential parties. Unless otherwise specified, all functions are made public by default
Private:
can only be called by the main contract itself. Although it’s not the default, it is generally good practice to keep your functions private unless a scope with more visibility is needed
StateMutability:
defines the behaviour of functions and how they interact with data stored on the blockchain
Pure:
function that doesn't read or modify the variables of the state
Constant:
have their values assigned at compile time and will not allow for any modifications at runtime
Payable:
ensures that the function can send and receive Ether
View:
only reads but doesn't alter the state variables defined in the contract
Override:
lets developers change how a function in the parent contract is implemented in the derived class.
UserDefinedTypeName:
Name of the defined type
Event Definition:
an inheritable member of a contract. An event is emitted, it stores the arguments passed in transaction logs. These logs are stored on blockchain and are accessible using address of the contract till the contract is present on the blockchain
Name:
Name of the event
Parameters:
Parameters of the event
Variable Declaration:
variable for the event
isAnonymous:
events can only be filtered through contract address
Enum Definition:
user-defined data types that restrict the variable to have only one of the predefined values.
Name:
Name of the enum
Members:
value of the enum
Enum Value
Name:
name of the values in enum
Interface
Function signatures without the function definition implementation
Library
A different type of smart contract that contains reusable code. Once deployed on the blockchain (only once), it is assigned a specific address and its properties / methods can be reused many times by other contracts in the Ethereum network
Abstract
Contains at least one function without any implementation. Such a contract is used as a base contract
Import
Import other Solidity files and we can access its code within the current Solidity file and code